📓 3.3.0.02 Introduction to Databases
Before we begin connecting databases to our MVC apps, let's explore how databases work. This lesson will walk through basic database vocabulary and discuss how most standard databases organize information.
Database Structure
If you've ever used Microsoft Excel or other similar software to create spreadsheets, you already know something about how databases are structured. Databases are like a bunch of linked spreadsheets. Each "spreadsheet" of information is called a table.
Example Databases
Let's make a mock database table that includes names and phone numbers:
contacts ------- id | name | phone ---+---------+----------- 1 | Ahmed | 9165551212 2 | Jessica | 3235551212 3 | Sofia | 4155551212
Just like a spreadsheet, this database table has a name. This one is called
contacts.It has three columns:
id,nameandphone.It also contains three entries, or rows: one for
Ahmed, one forJessica, and a third forSofia. Each row contains anid,nameandphonenumber corresponding to this person.
Here's another example. This one contains booleans:
things_in_portland ------------------ id | category | in_portland ---+--------------+------------ 1 | sunshine | false 2 | moonshine | true 3 | shiny things | true
This table is titled
things_in_portland.Its columns are
id,category, andin_portland.It contains three rows.
C# Classes and Database Tables
Let's consider another basic example. This time, we'll explore how components of a database will work with logic from our C# applications.
Let's pretend we're organizing a music festival. The festival has multiple music stages and many different artists. We've been asked to create an app that will create a program for the festival by tracking the following information:
- Which artists are playing at the festival, including;
- Their name.
- How many members their band has.
- The genre of music they play.
- Which stages the festival has, including;
- The name of the stage.
- The location of the stage in the festival.
- The audience capacity at that stage.
Before we consider our database, let's first determine how we'd represent this information in C# code. We should immediately think of two classes for this application: Stage and Artist. To keep it simple, our Stage class has three properties: Name, Location, and Capacity. Our Artist class also has three properties: Name, Members, andGenre.
Here are the classes for Artist and Stage:
class Stage
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Location { get; set; }
public int Capacity { get; set; }
}
class Artist
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Members { get; set; }
public string Genre { get; set; }
}
In order to store these objects in a database, our database tables would be structured like this:
stages table
artists table
The C# class name matches the name of the corresponding database table.
Each class property is represented with a column on the table.
Classes in C# are singular and capitalized. However, corresponding database tables are plural and lower case. This is standard naming convention.
Rows and Columns
When we create new C# objects, we assign each object property a value in the constructor. We do the same when we store data in a database: assign values to each property. In effect, the equivalent of an object in the database is the row with each property value being stored in a property column.
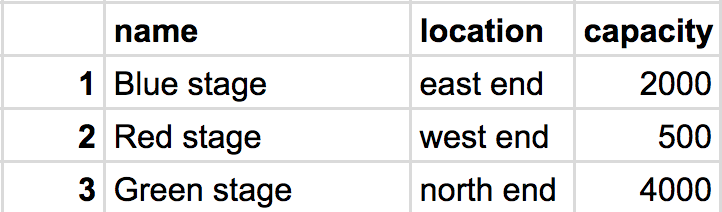
stages Table
artists Table
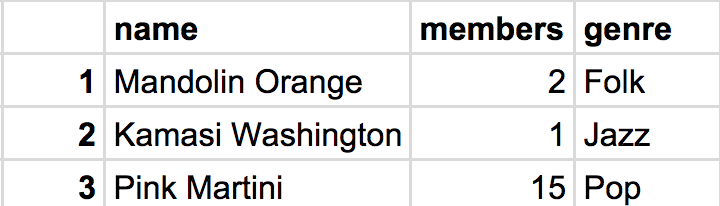
Here, each row in the database represents a C# Artist or Stage object. Each of the object's properties is stored under the database column of the same name.
Primary Keys
When database rows are added, the first column (usually called id) is the primary key. This is a unique ID for that specific row on that specific table. It will never be repeated or reused in the table. Our database will make it for us automatically.
In our example, the Blue stage has a primary key of 1 on the stages table and Pink Martini has a primary key of 3 on the artists table. Similar to the manner we used Id properties to locate specific objects last section, these primary database keys are used to locate specific database entries.