📓 3.2.0.17 Redirecting to HTTPS and Issuing a Security Certificate
In this lesson, we'll learn how to enable HTTPS redirection and set up security certificates for our web apps during development. While it's not always necessary to use HTTPS during development, it does provide additional security.
As we learned in previous lessons, HTTP is a protocol to transfer documents (like HTML) between web browsers (also called "clients") and web servers (also called "servers"). All modern and widely-used browsers use HTTP. However, HTTP is not secure, which is why HTTPS was developed. The "S" in HTTPS stands for "secure" as HTTPS encrypts all communication between a client and a server.
Web apps don't need to use HTTPS, though it is considered best practice to do so. In this lesson we'll learn how to enable HTTPS redirection and set up security certificates for our ASP.NET Core apps. Later in the course, we'll learn how to enable HSTS, which enforces that a website should only be accessed through HTTPS, and not merely redirected to from HTTP.
Enabling HTTPS Redirection
If you haven't noticed, ASP.NET Core offers two ports to access our web app, one for HTTP and the other for HTTPS:
- HTTP at http://localhost:5000
- HTTPS at https://localhost:5001
So far, we've primarily accessed http://localhost:5000, but we can access either. To increase security in our app, we can configure our host to redirect to HTTPS when our web app is accessed via HTTP. To do this, we need to update Program.cs to add a middleware to our request pipeline. We'll add app.UseHttpsRedirection(); right below the creation of our WebApplication host app. Check out the code snippet below that shows the updated Program.cs from the "Friend Letter" project.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace FriendLetter
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
WebApplicationBuilder builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews();
WebApplication app = builder.Build();
// app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseRouting();
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"
);
app.Run();
}
}
}
Note that if we included the app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); middleware, we'd need to add app.UseHttpsRedirection(); right below it.
Now with just one new line of code, if we access our application at http://localhost:5000, we'll be redirected to https://localhost:5001. Pretty neat! We recommend that you enable HTTPS redirection for all of your ASP.NET Core web apps going forward.
Issuing and Trusting a Security Certificate
For HTTPS to work, we need to have a security certificate set up for our web apps. The security certificate is a digital certificate that verifies the identity of a website and handles encrypting the data that's transferred between the website ("client") and the web server ("server"). These certificates are issued by certification authorities and follow specific protocols for encryption (see SSL and TLS for more information).
Typically security certificates are set up during the process of hosting a web app. However, when using HTTPS in development, we need to set one up via .NET. Fortunately, this is very easy to do via the command line.
First let's learn how to recognize when there are issues with the security certificate. If we ever navigate to https://localhost:5001/ and we get the following message in the browser, that means that there's something wrong with our security certificate:
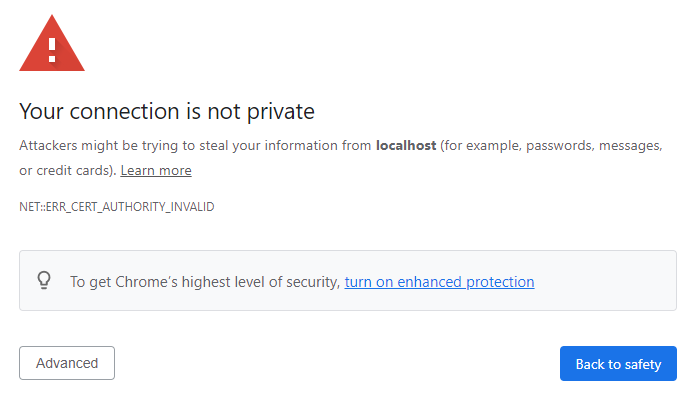
The good thing to note is that it's very easy to fix this issue. Simply open your terminal and enter the following command:
$ dotnet dev-certs https --trust
Note that if you are taking classes in person at Epicodus, you do not need to run this command on the campus mac computers.
When we enter this command, we should see a pop-up box with a message asking yet whether we want to proceed. Select the button that corresponds to 'yes', and then you'll have a trusted certificate for HTTPS during development.
The next step is to restart your web browser to clear its cache, then navigate to https://localhost:5001/ to confirm that you can access the site without error.
Note that with the original download of the .NET 6 SDK, we also downloaded a security certificate. So the process outlined above doesn't create a new one, but trusts the already existing certificate.
And with that, we're ready to go! You should only have to do this once for your computer, or after a major update like upgrading to a new version of .NET.
Granting Keychain Access For Students Working on Macs
With app.UseHttpsRedirection(); enabled, students who are working on macs in person or remotely may be asked to be granted keychain access to get the details of the dev cert for each new application they create. The request will pop up after you run your web app with dotnet watch run, and it will look similar to the following image with some details being different.
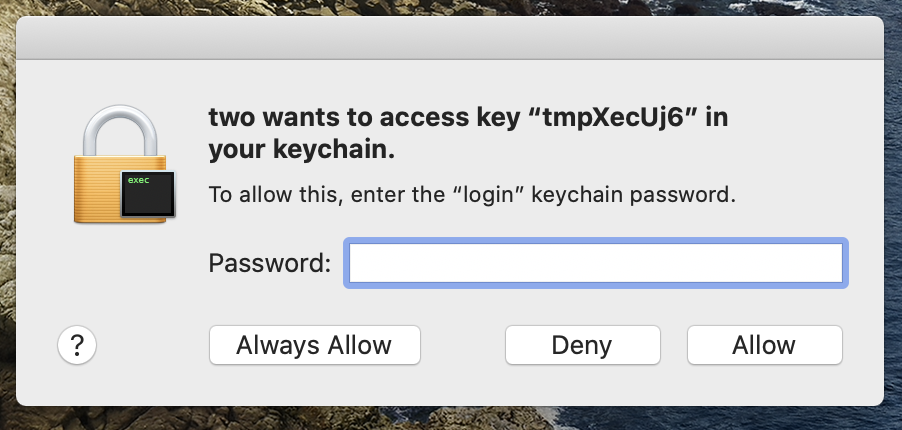
If you see this request after running your app, enter in your password and select "always allow". For mac computers on campus at Epicodus, the password is "epicodus".
If for some reason you cannot grant access to your keychain and this is preventing you from running your application in the browser, you can always use HTTP instead of HTTPS. Simply remove the line app.UseHttpsRedirection(); from Program.cs.
Don't Have a Security Certificate?
Not having a certificate at all is extremely unlikely. You'll know you don't have a security certificate, because you won't be able to access localhost via HTTPS at all. In this case, to generate a security certificate, run the following command:
$ dotnet dev-certs https
And then trust the certificate with this command:
$ dotnet dev-certs https --trust
You can also clear all existing certificates and check whether you have one issued to begin with. To see all possible commands and tools for dev-certs, enter the following command into your command line:
$ dotnet dev-certs https --help
To learn more about the dev-certs tool, visit the Microsoft documentation on dev-certs.
To learn more about trusting the ASP.NET Core development security certificate, visit this Microsoft documentation.